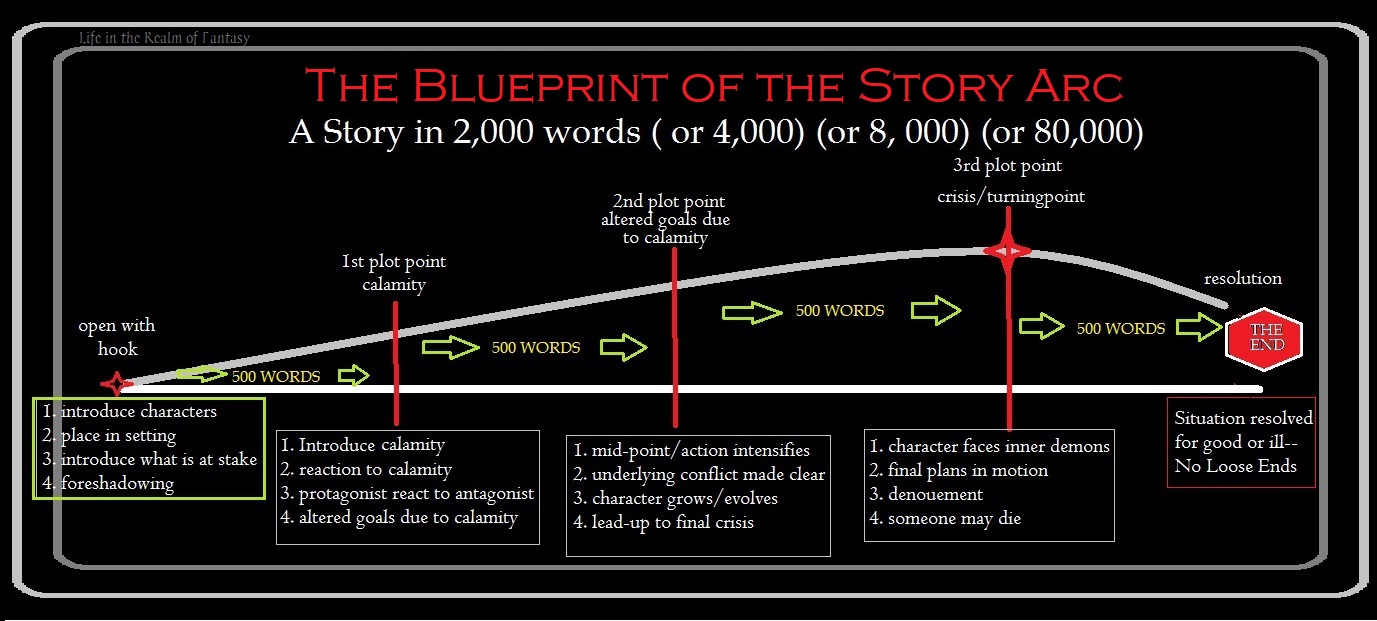
Artist: Jan Brueghel the Younger (1601–1678)
Title: the Bird Concert
Date: between circa 1640 and circa 1645
Medium: oil on copper
Dimensions: height: 13.2 cm (5.1 in); width: 17.9 cm (7 in)
Collection: Herzog Anton Ulrich Museum
Today we are taking a second look at one of my favorite paintings of the 17th century.
What I love about this painting:
This is one of my all-time favorite paintings. Jan Brueghel the Younger was a master who stood out in a dynasty of masters. The Brueghel family descended from Pieter Brueghel the Elder, and each generation left behind works that enchant us to this day.
I love this fantasy of birds, a renaissance view of what true harmony could be.
Brueghel gives us a joyous, surreal exploration of all the birds the artist had ever seen in his native Antwerp, and many rare birds that he could only imagine. He has gathered birds from all over the world into a mystical, fairytale glen, posing them around a songbook.
They are learning to sing a in a language they all can understand, a wonderful allegory of the aspirations of the artist for humanity in the turbulent times during which he lived.
This painting also celebrates the new discoveries made by European explorers, as Brueghel had only seen scientific drawings of many of these birds. Even though he hadn’t seen some of these birds personally, he paints them as if they are before him.
The amazing flock of birds gathered here gives us an insight into the mind and sense of humor of Jan Brueghel the Younger, a man not too different from us even though he lived over 300 years ago.
This composition must have been important to Brueghel and says something about him. He went to the expense of getting copper as the base upon which he painted this scene. He was comfortable but not rich, so that tells me he intended this painting to last, to be something he would be remembered for.
About the medium of Oil on Copper, via Wikipedia:
Oil on copper paintings were prevalent in the mid sixteenth century in Italy and Northern Europe. The use of copper as a substrate for an oil painting dates back to Medieval times. The Flemish masters and other artists including Jan Breughel the Elder, Claude, El Greco, Guido Reni, Guercino, Rembrandt, Carlo Saraceni, Ambrosius Bosschaert II, Copley Fielding and Vernet painted on copper. They favored copper for its smooth surface which allowed fine detail, and its durability. Copper is more durable than canvas or wood panel as a support for oil painting, as it will not rot, mildew or be eaten by insects. Contemporary painters also use copper as a base for paintings, some of them allowing the metal or patina to show through.
The old masters prepared the copper for painting first by rubbing it with fine pumice abrasive. The copper surface was then treated with garlic juice which is believed to improve adhesion of the paint. Finally a white or grey ground layer of oil paint was applied as a primer. After drying the copper panel was ready for the artist to begin painting. Later artists used the patina process, in which the copper is oxidized with the use of various acidic solutions, as part of the art work itself. The resulting patina or verdigris includes darkening of the metal, green and blue tones, depending on the chemical solution used. Patina is characterized by beautiful, variated patterns and textures which occur on the metal’s surface. [1]
About the Artist, via Wikipedia:
Jan Brueghel the Younger was born in Antwerp on 13 September 1601 as the son of Jan Brueghel the Elder and Isabella de Jode. His mother was the daughter of the cartographer, engraver and publisher Gerard de Jode. He trained and collaborated with his father in his workshop. His father was a friend and close collaborator of Peter Paul Rubens. Brueghel likely assisted with his father’s large-scale commissions.
On the wishes of his father, he traveled around 1622 to Milan where he was welcomed by Cardinal Federico Borromeo. The cardinal was a patron and friend of his father who had met in Rome about 30 years earlier. In what was likely an act of rebellion against his father, he went to Genoa where he stayed with his cousins, the Antwerp painters and art dealers Lucas de Wael and Cornelis de Wael. Their mother was a sister of Brueghel’s mother. At the time his friend and fellow Antwerp artist Anthony van Dyck was also active in Genoa. He later worked in Valletta on Malta in 1623. From 1624 to 1625 he also resided in Palermo on Sicily at the time when van Dyck was also working there.
Brueghel learned that his father had died on 13 January 1625 from cholera only after his return to Northern Italy in Turin. Wanting to return to Antwerp immediately, he had to delay his departure for 16 days due to a severe fever. After recovering from his illness, he set off for his homeland by way of France. In Paris he met the Antwerp art dealer and painter Peter Goetkint the Younger, who was the son of Peter Goetkint the Elder, the master of Jan’s father. Goetkint was eager to return to Antwerp because his wife was expected to deliver a baby soon. The child was born on 25 August, the day on which Breughel arrived in Antwerp with his traveling companion who himself died a few days later.
Brueghel took over the management of his father’s workshop, sold the finished works of his father and finished some of his father’s unfinished paintings. In the Guild year 1624-1625, Brueghel became a master painter of the Guild of Saint Luke of Antwerp.
In 1626 he married Anna Maria Janssens, daughter of Abraham Janssens, a prominent history painter in Antwerp. He continued to operate the large workshop of his father. He became dean of the Guild of Saint Luke in 1630. That same year he was commissioned by the French court to paint a series of paintings on the life of Adam. It seems that his studio declined after this period and that he started to paint smaller scale paintings which commanded lower prices than those produced earlier.
In later years, he worked independently in Paris in the 1650s and produced paintings for the Austrian court in 1651. He is recorded again in Antwerp in 1657 where he remained until his death. [2]
Credits and Attributions:
[1] Wikipedia contributors, “Oil on copper,” Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Oil_on_copper&oldid=1060711380 (accessed JAug 7, 2025).
[2] Wikipedia contributors, “Jan Brueghel the Younger,” Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Jan_Brueghel_the_Younger&oldid=1086952033 (accessed Aug 7, 2025).
Image: The Bird Concert by Jan Brueghel the Younger ca. 1640 -1645, PD|100. Wikimedia Commons contributors, “File:Bruegel Vogelkonzert@Herzog Anton Ulrich Museum (1).JPG,” Wikimedia Commons, the free media